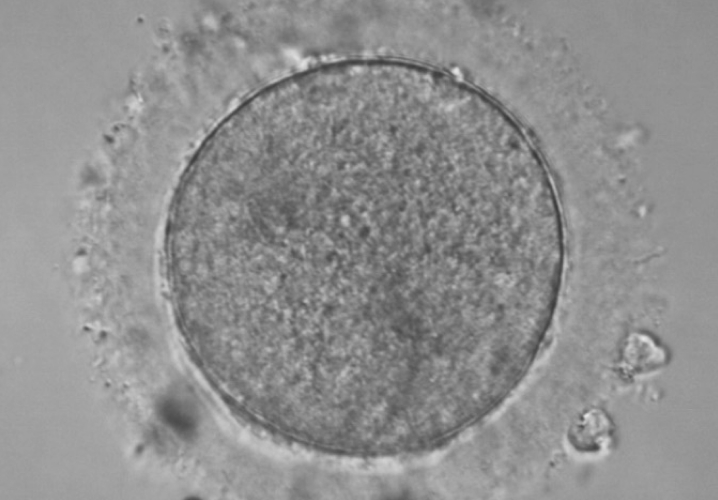
Since MFC’s inception, we’ve recognized that some individuals undergoing IVF have unique clinical and personal situations which need to be factored into treatment approaches. As such, we have always made it a top priority to offer the latest IVF adjuncts that are customized to meet each patient’s individual needs. Honoring our commitment to true personalized medicine we are proud to offer the following:
IVF Variations
treatment as individual as you
moderate ivf
Moderate IVF focuses on quality, not quantity. The goal of moderate (aka mini) IVF is to stimulate the ovary with a smaller amount of medication to promote the development of a smaller quantity of fertilizable eggs. This approach is sometimes considered at the extremes of reproductive age (less than 30 or older than 43 years old).
Key features
Less medication than traditional ivf (typically ~30-50%)

Goal: 3-4 mature follicles (each mature follicle normally contains 1 fertilizable egg)
Who it may be for
- Very young age desiring only 1 child
- Low responders or severely diminished ovarian reserve
- Sensitivities to stimulation medications/hormone concerns
- Immunologic medical problems or cancers
- Specific hormone profiles
How it works
The end result
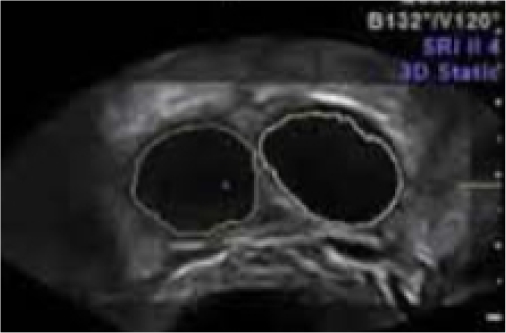
Moderate IVF: ~2 mature follicles on each ovary
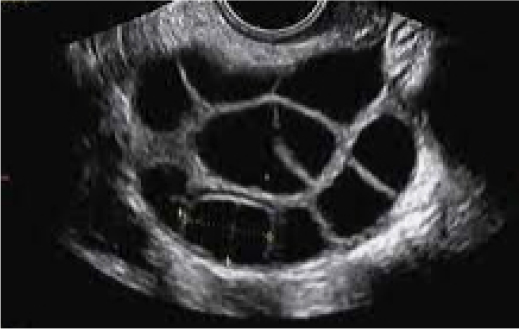
Traditional IVF: ~4-8 mature follicles on each ovary
intravaginal culture (ivc)
Intravaginal culture (IVC) uses the INVOcell device, a small (2.5 x 4.5 cm) capsule that houses eggs, sperm and embryos while resting inside a vagina for 3-5 days. Unlike conventional in vitro fertilization (IVF), where embryo culture takes place inside a laboratory incubator, INVOcell utilizes the women’s vagina as a natural incubator to support embryo development. This novel technology offers patients a more connected approach to achieving pregnancy while aligning with the prevailing goal of keeping costs down.
Key features

Moderate ovarian stimulation with a goal of 6-8 folicles

The embryo culture component of the IVF process occurs in the body instead of the lab
Who it may be for
- Patient desiring an added connection to the journey
- Patients prioritizing cost containtment
- Dual IVF
- Aligns well with smaller family size goals and no PGT (preimplantaion genetic testing)
How it works
the difference

The INVOcell unit (foreground) and the holding device (background)

Our in-house time lapse IVF incubator: “the Geri”
in vitro maturation (ivm)
In vitro maturation (IVM) describes a process whereby immature eggs, those not yet ready to be fertilized by a sperm, undergo their final developmental stages in the laboratory. Under normal conditions and in response to hormone stimulation, follicles (ovarian structures that house eggs) enlarge and release mature (fertilizable) eggs. With IVM, eggs are released from small follicles at an immature stage of development. After maturation in the laboratory, IVM eggs can be fertilized and used to achieve pregnancy in the same way as in IVF.
Key features

No (or minimal) ovarian stimulation
Goal: maximum number of immature eggs retrieved from small follicles
Who it may be for
- Prior IVF failures due to egg maturation problems
- Ovarian resistance to injectable stimulation medications
- Medical contraindications to ovarian stimulation
- New cancer diagnosis desiring fertility preservation
- Polyfollicular ovaries, normal body habitus, <35 years old
How it works
the difference

In traditional ivf the goal is large follicles (achieved through medication use)
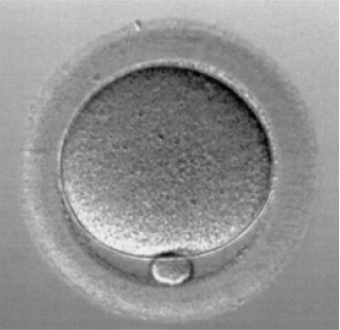
Large follicles contain mature eggs (eggs that are immediately ready to receive sperm when released from the ovary)
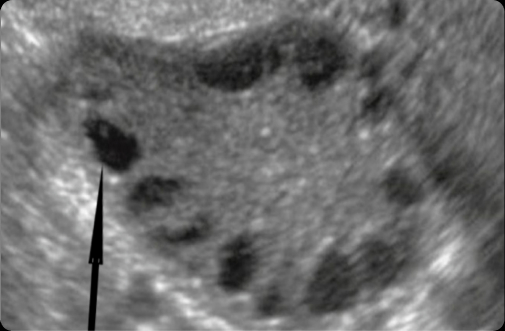
Small (unstimulated) follicles house immature (underdeveloped) eggs
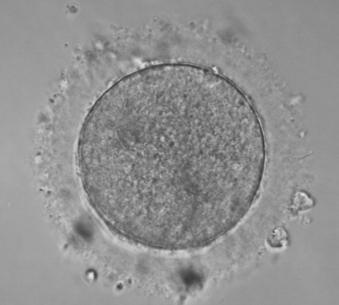
Small follicles contain immature eggs that need to be matured in laboratory